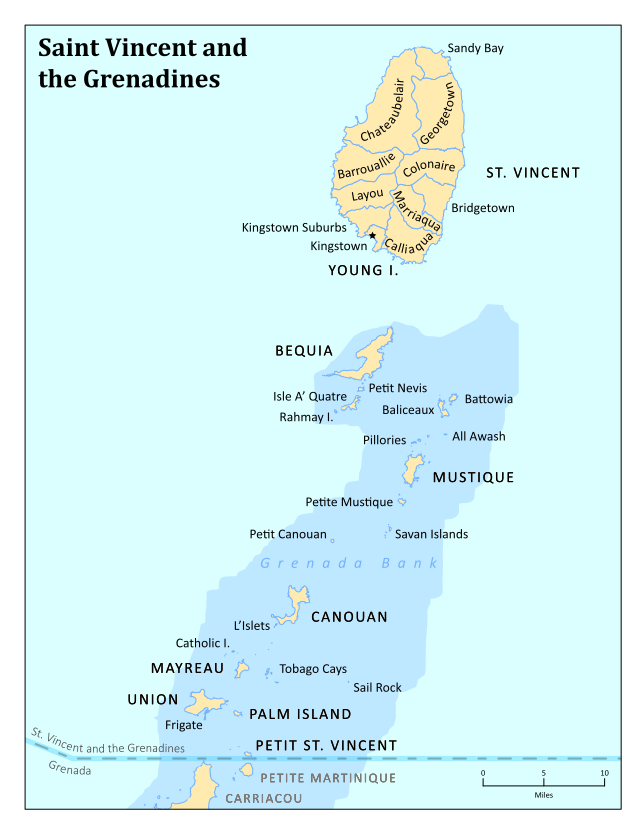
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is an island state in the Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, an island arc of the Caribbean Sea in North America.
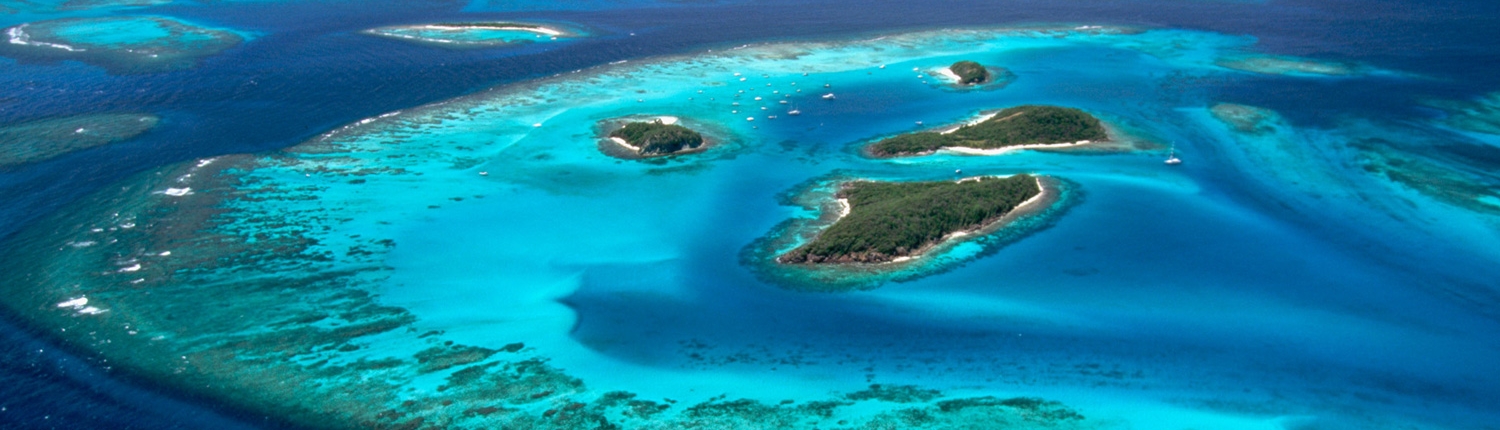
The country consists of the main island of Saint Vincent and the northern two-thirds of the Grenadines, a chain of small islands stretching south from Saint Vincent to Grenada.
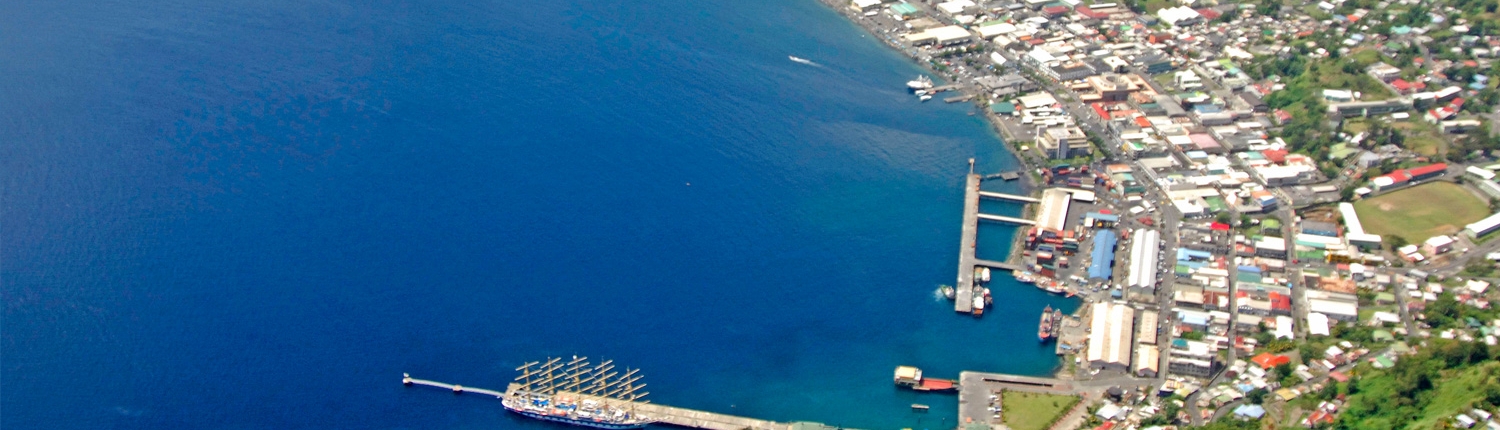
Its total land area is 390 km² of which 342.7 km² is the main island of Saint Vincent. The country’s capital is at Kingstown on Saint Vincent.
- Northernmost point: Porter Point
- Southernmost point: Petit Saint Vincent
- Westernmost point: Union Island, Grenadines Parish
- Easternmost point: Battowia island, Grenadines Parish
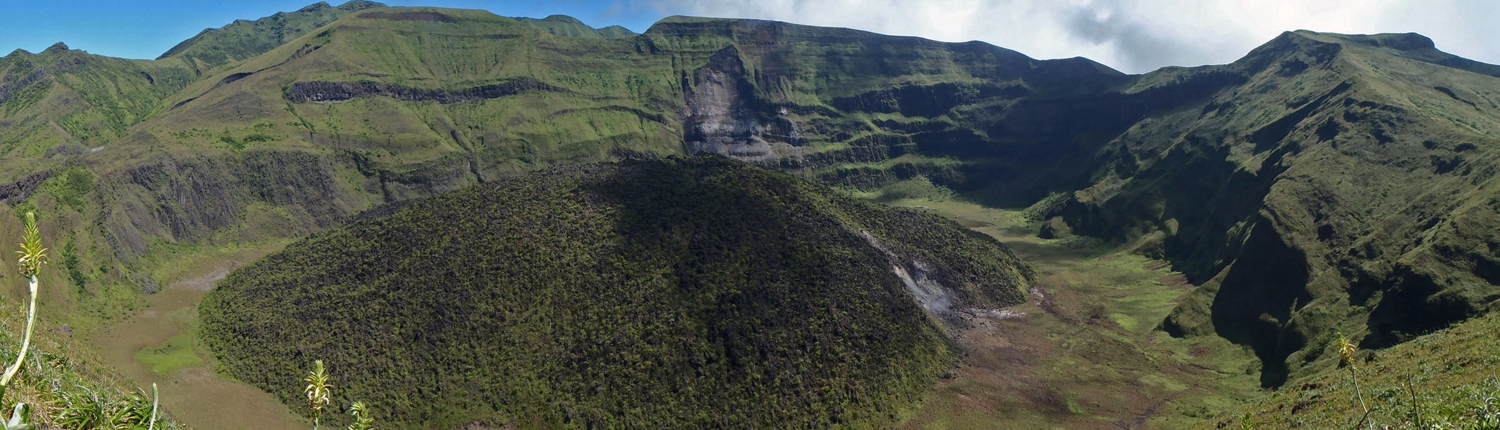
The main island of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is Saint Vincent. Its geography is mostly mountainous and includes very little level ground. There is also a large difference between the coastlines on each side of the island. The windward side is very rocky, while the leeward side consists of many sandy beaches and has many more bays. The island’s as well as the country’s highest peak is the volcanic Soufrière at 1,234 m. There are several tiny islets offshore of Saint Vincent including Young Island and the Cow And Calves Islands.